0 前言
一个高性能的 Bash 磁盘分析脚本,用于快速定位磁盘空间占用问题.
1 功能特性
-
子目录占用排行
- 显示占用超过 10% 的子目录
- 对占用超过 50% 的目录自动递归分析
- 树形结构展示,一目了然
-
大文件查找
- 查找超过指定大小的文件(默认 1024MB)
- 显示 Top 5 大文件
- 显示文件大小,修改日期,所有者
-
性能优化
- 使用关联数组缓存目录大小
- 一次扫描,多次查询
- 无临时文件,减少 I/O 开销
2 使用方法
2.1 脚本内容
#!/bin/bash
# ==============================================================================
# 磁盘分析脚本 (性能优化版)
# 功能: 1. 子目录占用排行(>10%,自动递归>50%) 2. 大文件 Top 5
# 用法: ./disk_analyze.sh [目录] [大文件阈值MB]
# 优化: 使用关联数组索引缓存,减少 du 调用,消除临时文件
# ==============================================================================
set -o pipefail
# --- 参数 ---
TARGET_DIR="${1:-$(pwd)}"
LARGE_FILE_LIMIT_MB="${2:-1024}"
TOP_N=5
SHOW_THRESHOLD=10
RECURSE_THRESHOLD=50
if ! [[ "$LARGE_FILE_LIMIT_MB" =~ ^[0-9]+$ ]]; then
echo "错误: 大文件阈值MB 必须是整数, 当前: $LARGE_FILE_LIMIT_MB"
exit 1
fi
# 转为绝对路径
if [ -d "$TARGET_DIR" ]; then
TARGET_DIR=$(cd "$TARGET_DIR" && pwd)
else
echo "错误: 目录 $TARGET_DIR 不存在!"
exit 1
fi
# --- 颜色 ---
RED='\033[0;31m'
GREEN='\033[0;32m'
YELLOW='\033[1;33m'
CYAN='\033[0;36m'
BLUE='\033[0;34m'
BOLD='\033[1m'
NC='\033[0m'
# --- 目录索引(核心优化:一次扫描,多次查询)---
declare -A DIR_SIZE=()
declare -A DIR_CHILDREN=()
# 进度显示函数
show_progress() {
local count="$1"
local current_path="$2"
local spinner=('⠋' '⠙' '⠹' '⠸' '⠼' '⠴' '⠦' '⠧' '⠇' '⠏')
local idx=$((count / 10 % 10))
# 截断过长的路径
local display_path="$current_path"
if [ ${#display_path} -gt 50 ]; then
display_path="...${display_path: -47}"
fi
printf "\r ${CYAN}${spinner[$idx]}${NC} 扫描中: ${YELLOW}%d${NC} 个目录 %-50s" "$count" "$display_path" >&2
}
build_dir_index() {
local root="$1"
DIR_SIZE=()
DIR_CHILDREN=()
local dir_count=0
local last_update=0
# du 默认只输出目录. 使用 -0 避免路径含空格/换行时被 read 拆分.
while IFS=$'\t' read -r -d '' size path; do
[ -z "$size" ] && continue
DIR_SIZE["$path"]="$size"
dir_count=$((dir_count + 1))
# 每 100 个目录或每秒更新一次进度
if (( dir_count - last_update >= 100 )); then
show_progress "$dir_count" "$path"
last_update=$dir_count
fi
if [ "$path" != "$root" ]; then
local parent="${path%/*}"
[ -z "$parent" ] && parent="/"
DIR_CHILDREN["$parent"]+="$path"$'\n'
fi
done < <(du -b -0 -x "$root" 2>/dev/null)
# 清除进度行,显示完成信息
if (( dir_count > 0 )); then
printf "\r ${GREEN}✓${NC} 扫描完成: ${YELLOW}%d${NC} 个目录%-50s\n" "$dir_count" "" >&2
fi
}
# --- 工具函数(优化:使用 Bash 原生算术替代 awk)---
human_size() {
local bytes="${1:-0}"
[ -z "$bytes" ] || [ "$bytes" = "0" ] && echo "0B" && return
local div unit
if (( bytes >= 1073741824 )); then
div=1073741824
unit="G"
elif (( bytes >= 1048576 )); then
div=1048576
unit="M"
elif (( bytes >= 1024 )); then
div=1024
unit="K"
else
echo "${bytes}B"
return
fi
local tenths=$(( (bytes * 10 + div / 2) / div ))
printf "%d.%d%s" $((tenths / 10)) $((tenths % 10)) "$unit"
}
# 显示目录下 Top N 文件/子目录(优化:使用 awk 插入排序替代 sort | head)
show_top_items() {
local dir="$1"
local prefix="$2"
local dir_size="$3"
printf "${prefix}${BLUE}┌─ 热点目录: %s${NC}\n" "$dir"
printf "${prefix}${BLUE}│${NC}\n"
while IFS='|' read -r size type name; do
[ -z "$size" ] && continue
local pct=0
if (( dir_size > 0 )); then
pct=$(( (size * 100 + dir_size / 2) / dir_size ))
fi
if [ "$type" = "D" ]; then
printf "${prefix}${BLUE}│${NC} %-30s ${CYAN}%8s %3s%%${NC} [目录]\n" "$name" "$(human_size "$size")" "$pct"
else
printf "${prefix}${BLUE}│${NC} %-30s ${YELLOW}%8s %3s%%${NC} [文件]\n" "$name" "$(human_size "$size")" "$pct"
fi
done < <(
{
children="${DIR_CHILDREN["$dir"]}"
if [ -n "$children" ]; then
while IFS= read -r child; do
[ -z "$child" ] && continue
size="${DIR_SIZE["$child"]}"
[ -z "$size" ] && continue
printf '%s|D|%s\n' "$size" "${child##*/}"
done <<< "$children"
fi
find -L "$dir" -mindepth 1 -maxdepth 1 -xdev -type f -printf '%s|F|%f\n' 2>/dev/null
} | awk -v n="$TOP_N" -F '|' '
BEGIN { count=0 }
{
size=$1+0
line=$0
pos=count+1
for (i=1; i<=count; i++) {
if (size > sizes[i]) { pos=i; break }
}
if (pos > n) next
if (count < n) count++
for (j=count; j>pos; j--) {
sizes[j]=sizes[j-1]
lines[j]=lines[j-1]
}
sizes[pos]=size
lines[pos]=line
}
END { for (i=1; i<=count; i++) print lines[i] }
'
)
printf "${prefix}${BLUE}└────────────────────────────────────────────${NC}\n"
}
# ==============================================================================
# [1] 子目录占用分析 (递归) - 优化:使用缓存索引
# ==============================================================================
analyze_directory() {
local dir="$1"
local prefix="$2"
local parent_size="$3"
# 获取当前目录总大小(从缓存)
local total_size="${parent_size:-${DIR_SIZE["$dir"]}}"
[ -z "$total_size" ] || [ "$total_size" -eq 0 ] && return
# 收集符合条件的子目录(从缓存)
local children="${DIR_CHILDREN["$dir"]}"
[ -z "$children" ] && return
local items=()
while IFS= read -r path; do
[ -z "$path" ] && continue
local size="${DIR_SIZE["$path"]}"
[ -z "$size" ] && continue
local pct=$(( (size * 100 + total_size / 2) / total_size ))
[ "$pct" -lt "$SHOW_THRESHOLD" ] && continue
items+=("$size|$pct|$path")
done <<< "$children"
# 如果没有符合条件的子目录,直接返回
[ ${#items[@]} -eq 0 ] && return
local sorted=()
mapfile -t sorted < <(printf '%s\n' "${items[@]}" | grep -v '^$' | LC_ALL=C sort -t'|' -k1,1nr)
local count=${#sorted[@]}
local i=0
for item in "${sorted[@]}"; do
# 跳过空项
[ -z "$item" ] && continue
i=$((i + 1))
local size="${item%%|*}"
local rest="${item#*|}"
local pct="${rest%%|*}"
local path="${rest#*|}"
# 防止空值导致的整数比较错误
[ -z "$size" ] && continue
[ -z "$pct" ] && pct=0
[ -z "$path" ] && continue
# 判断是否是最后一个
local is_last=0
[ "$i" -eq "$count" ] && is_last=1
# 选择树形符号
local branch
local child_prefix
if [ $is_last -eq 1 ]; then
branch="└── "
child_prefix="${prefix} "
else
branch="├── "
child_prefix="${prefix}│ "
fi
# 根据占比选择颜色
local color="$CYAN"
[[ "$pct" =~ ^[0-9]+$ ]] && [ "$pct" -ge 60 ] && color="$RED"
[[ "$pct" =~ ^[0-9]+$ ]] && [ "$pct" -ge 40 ] && [ "$pct" -lt 60 ] && color="$YELLOW"
# 显示目录名
local name="${path##*/}"
printf "${prefix}${branch}%-20s ${color}%8s %3s%%${NC}\n" "$name" "$(human_size "$size")" "$pct"
# 占用超过阈值则递归
if [[ "$pct" =~ ^[0-9]+$ ]] && [ "$pct" -ge "$RECURSE_THRESHOLD" ]; then
local sub_size="$size"
# 检查子目录是否还有超过阈值的项(从缓存)
local has_more=0
local sub_children="${DIR_CHILDREN["$path"]}"
if [ -n "$sub_children" ] && (( sub_size > 0 )); then
while IFS= read -r sub_item_path; do
[ -z "$sub_item_path" ] && continue
local sub_item_size="${DIR_SIZE["$sub_item_path"]}"
[ -z "$sub_item_size" ] && continue
local sub_pct=$(( (sub_item_size * 100 + sub_size / 2) / sub_size ))
if [ "$sub_pct" -ge "$RECURSE_THRESHOLD" ]; then
has_more=1
break
fi
done <<< "$sub_children"
fi
if [ "$has_more" -eq 1 ]; then
# 继续递归
analyze_directory "$path" "$child_prefix" "$sub_size"
else
# 已到最深层,显示 Top N
printf "${child_prefix}\n"
show_top_items "$path" "$child_prefix" "$sub_size"
fi
fi
done
}
analyze_directories() {
printf "${YELLOW}[1] 子目录占用分析 (>%d%%, 递归>%d%%)${NC}\n" "$SHOW_THRESHOLD" "$RECURSE_THRESHOLD"
printf "────────────────────────────────────────────────────────\n"
local start_time=$(date +%s)
# 核心优化:一次构建索引
build_dir_index "$TARGET_DIR"
local total_size="${DIR_SIZE["$TARGET_DIR"]}"
printf " ${BOLD}%-20s %8s${NC}\n" "$TARGET_DIR" "$(human_size "$total_size")"
analyze_directory "$TARGET_DIR" " " "$total_size"
printf "\n 耗时: $(($(date +%s) - start_time))秒\n\n"
}
# ==============================================================================
# [2] 大文件查找(优化:使用 awk 插入排序替代 sort | head)
# ==============================================================================
find_large_files() {
printf "${YELLOW}[2] 大文件 Top ${TOP_N} (>${LARGE_FILE_LIMIT_MB}MB)${NC}\n"
printf "────────────────────────────────────────────────────────\n"
printf " ${BOLD}%-50s %-10s %-10s %-8s${NC}\n" "PATH" "SIZE" "DATE" "OWNER"
printf " %-50s %-10s %-10s %-8s\n" "--------------------------------------------------" "----------" "----------" "--------"
local start_time=$(date +%s)
local count=0
while IFS=$'\t' read -r size mtime owner path; do
[ -z "$size" ] && continue
count=$((count + 1))
printf " %-50s ${RED}%-10s${NC} %-10s %-8s\n" \
"$path" "$(human_size "$size")" "$mtime" "$owner"
done < <(
find "$TARGET_DIR" -xdev -type f -size +"${LARGE_FILE_LIMIT_MB}"M \
-printf '%s\t%TY-%Tm-%Td\t%u\t%p\n' 2>/dev/null | \
awk -v n="$TOP_N" -F '\t' '
BEGIN { count=0 }
{
size=$1+0
line=$0
pos=count+1
for (i=1; i<=count; i++) {
if (size > sizes[i]) { pos=i; break }
}
if (pos > n) next
if (count < n) count++
for (j=count; j>pos; j--) {
sizes[j]=sizes[j-1]
lines[j]=lines[j-1]
}
sizes[pos]=size
lines[pos]=line
}
END { for (i=1; i<=count; i++) print lines[i] }
'
)
[ $count -eq 0 ] && printf " ${GREEN}无超过 ${LARGE_FILE_LIMIT_MB}MB 的文件${NC}\n"
printf "\n 耗时: $(($(date +%s) - start_time))秒\n\n"
}
# ==============================================================================
# 主程序
# ==============================================================================
main() {
printf "\n"
printf "${BOLD}═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════${NC}\n"
printf "${BOLD} 磁盘分析: ${CYAN}%s${NC} [%s]${NC}\n" "$TARGET_DIR" "$(date '+%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')"
printf "${BOLD}═══════════════════════════════════════════════════════════${NC}\n\n"
analyze_directories
find_large_files
printf "${GREEN}完成${NC}\n\n"
}
main
2.2 使用方法
./disk_analyze.sh [目录] [大文件阈值MB]
2.3 参数说明
| 参数 | 默认值 | 描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 目录 | 当前目录 | 要分析的目标目录 |
| 大文件阈值 MB | 1024 | 大文件筛选阈值(单位:MB) |
2.4 使用示例
# 分析当前目录
./disk_analyze.sh
# 分析 /var 目录
./disk_analyze.sh /var
# 分析 /home 目录,查找超过 500MB 的文件
./disk_analyze.sh /home 500
3 效果展示
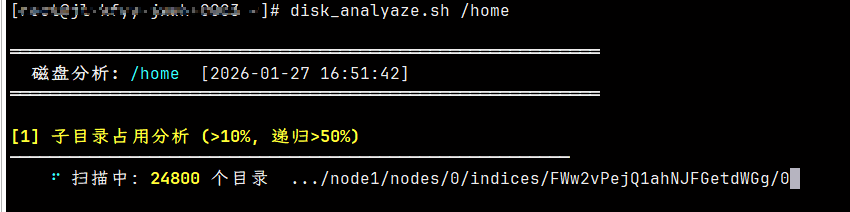
3.1 扫描进度
分析大目录时显示实时进度:
3.2 完整输出
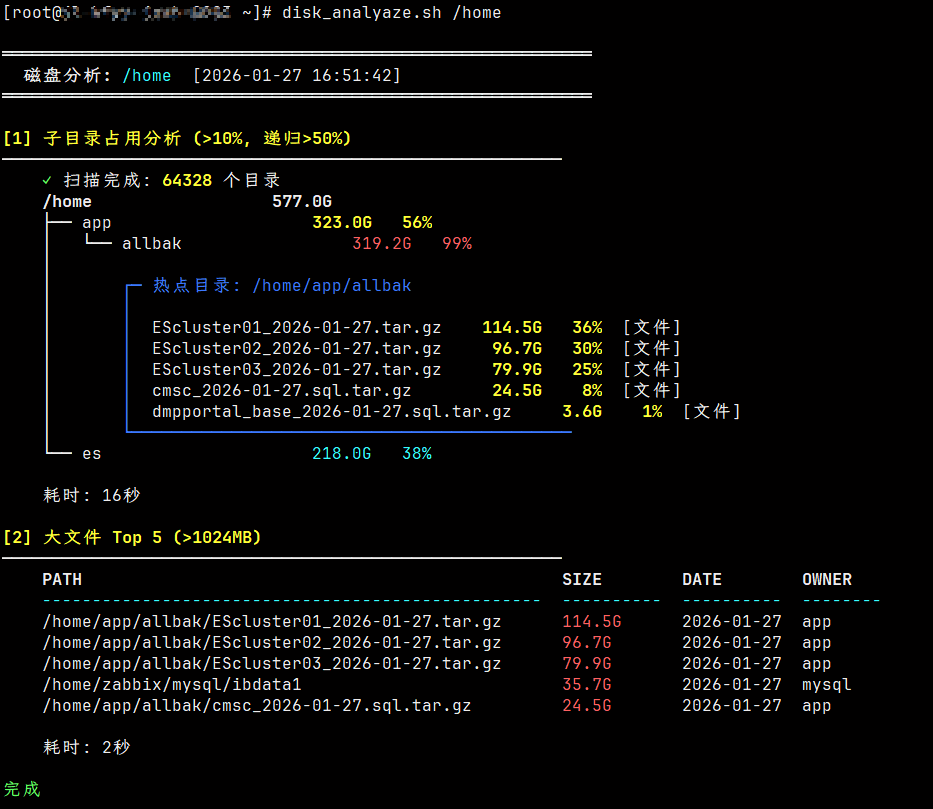
4 颜色说明
- 🔴 红色:占用 ≥60%,需重点关注
- 🟡 黄色:占用 40%-60%,建议检查
- 🔵 青色:占用 10%-40%,正常范围
5 环境要求
- Bash 4.0+(需要关联数组支持)
- GNU coreutils(du, find)
- awk
6 注意事项
- 脚本使用
-x参数,不会跨越文件系统边界 - 符号链接会被跟随(-L)
- 需要对目标目录有读取权限
以上.

